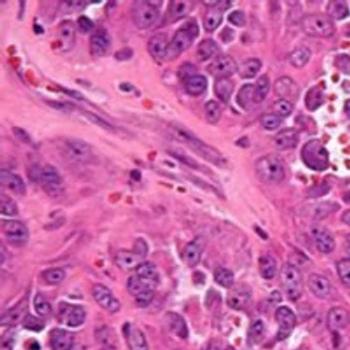
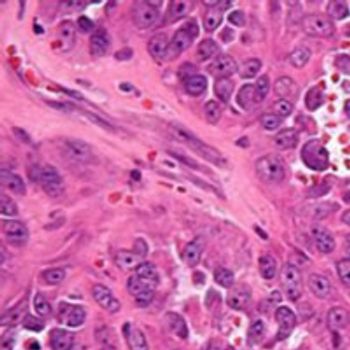
Investigators are evaluating the combination of telotristat ethyl and Lutathera with a goal to improve progression-free survival in patients with well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors in a randomized, phase 2 study that was highlighted during the 2020 NANETs Virtual Symposium.